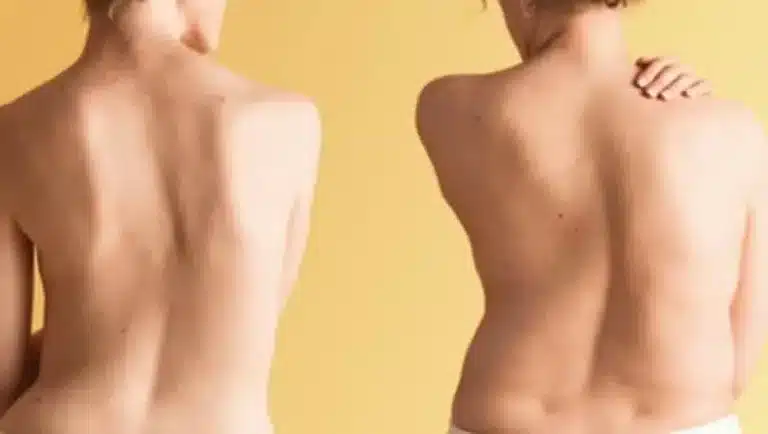
Adult Lumbar Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of more than 10 degrees in patients who have completed their skeletal development.
Adult scoliosis is mainly grouped in two types as degenerative and idiopathic.
Adult degenerative scoliosis is also known as “de novo scoliosis”. The vast majority of the patients are over 60 years old and it is more common in women.
As the causes of the disease, many factors play a role such as degeneration (calcification) of the lumbar vertebrae, osteoporosis and compression fractures.
The degree of curvature is below 20 degrees in most patients.
Adult idiopathic scoliosis, on the other hand, is the appearance of untreated adolescent scoliosis in upcoming ages. It is seen at younger ages and the degree of curvature is usually greater.
What are the Clinical Findings?
The most important clinical symptom of adult degenerative scoliosis is low back pain. This pain can be seen in the lower back only and/or as a pain spreading to legs.
In the adult idiopathic scoliosis group, degenerative changes, that is, calcification in the lumbar vertebrae, are less common due to being at younger ages.
The main complaint of these patients is more about their cosmetic appearance than low back pain. As age progresses, the complaint of pain due to degenerative changes gradually increases.
Which Examinations Need to be Done?
Detailed radiological examination is required for the patients with adult scoliosis and related complaints.
Especially, the patients who have loss of strength in their legs due to the disease should be examined with X-ray, MRI, CT and EMG should be performed to evaluate nerve conduction velocities.
Besides, in osteoporotic patients, bone density measurement should be performed with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), and measures should be taken to increase bone density when necessary.
What are the Medical Treatment Methods? To Whom is it Applied?
For the conservative treatment of adult scoliosis, there is no clear consensus method for treatment.
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, the use of berys, physical therapy and steroid injections can be considered as the most common methods.
Currently, conservative treatment is mostly applied to patients with mild symptoms that do not need surgery or who are too risky to be operated for other reasons.

What are the Surgical Treatment Methods?
In adult scoliosis, deciding on the surgical treatment and determining the method to be applied mainly depend on the patient’s complaints and physical examination findings.
A wide range of surgical treatment can be applied, from operations that are relatively easier, such as removal of disc hernias or bones that cause compression, to operations that require complete correction of the curvature using pedicle screws.
Here, factors such as the general condition of the patient, comorbidities, and neurological examination are also effective in deciding the method to be chosen.