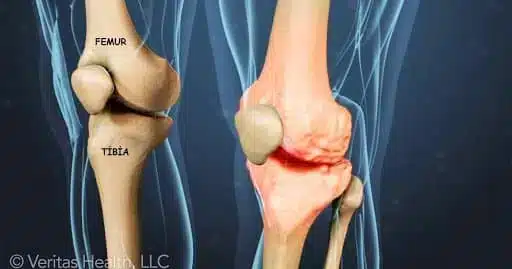
Our knee is made up of two smooth cartilages that slide over each other.
Between them are our meniscuses, cruciate ligaments, lateral ligaments and pellicles(perichondrium) inside the knee.
All of these can cause problems for us. But cartilage is the most problematic.
Because cartilage can’t regenerate itself. Cartilage damage can happen because of our genetic characteristics and as a result of direct impacts, falls, accidents or incorrect sports movements.

What is the Treatment of Cartilage Damages in the Knee?
Cartilage degredation in the knee can be classified as mild(minor) impairment and severe(major) impairment.
For mildly impaired patients, the first treatment method is to lose weight and strengthen the musculature around the leg and knee. In this way, flexible and strong muscle structure is obtained.
The following treatment methods for those are; especially during periods of pain, to eliminate the causes of pain by intervening with some drugs and to strengthen the muscle structure with exercise programs in the person’s daily life.
In the second group with severe degradation, there are some procedures performed for the knee.


One of the most common applications today is PRP.
Micro-Fracture Method
It is a method applied in cartilage injuries smaller than 3 cm. After the damaged area is cleaned of cartilage residues, holes are drilled into the bone at 5 mm intervals and extending a few mm deep. Through these holes, a path is opened for stem cells in the bone marrow to reach the damaged area. Stem cells that settle into the blood clot formed in the damaged area have the ability to transform into cartilage-like cells under the appropriate environment.
In recent years, implants called matrix have been developed so that this clot can better adhere to the damaged area and organize. These membrane-shaped tissues, mostly made of collagen, can be adhered to the damaged area after micro-fracture is performed.
It is necessary to protect the joint from the load by using crutches for six to eight weeks postoperatively, until new cartilage-like tissue is formed.
Similarly, for the formation of this cartilage repair tissue, it is necessary to move the joint slowly and in a controlled manner and to do small exercises for a few weeks in the postoperative period.
Mosaicplasty
It is the removal of cylindrical pieces of cartilage and bone, 6-8 mm in diameter and 15 mm in length, from the non-load-bearing area of the joint and transferring them to the damaged region in the load-bearing area. Like micro-fracture, this technique is applied for damage less than 4 cm. It is most commonly applied to the knee and ankle joints and can be done by arthroscopic or open method.
Its most important advantage is that a tissue in the normal cartilage structure is transferred to the damaged area.
The disadvantages are that a limited number of tissue transplants can be performed and the sacrifice of proper cartilage in another part of the joint, in order to transplant to the damaged area.
In very large damages, sometimes it may be necessary to take tissue from the opposite knee joint, which is intact.
Due to the nature of the technique, only 70% of the damaged area can be filled with the transplanted cartilage, and the area between the transplanted cylinders heals with a cartilage-like repair tissue. This technique is generally more successful in minor cartilage damages. It may be difficult to establish the normal shape of the joint in areas of major injury.
The postoperative period is similar to the micro-fracture method.
Cartilage Transplant
In recent years, the most researched and scientifically developed area is cartilage transplantation.
In this technique, while cartilage damage is detected by arthroscopy, a few mm of cartilage tissue in the form of chips is taken from the non-load-bearing region of the joint.
This tissue is processed in a laboratory environment under sterile conditions and is produced by multiplying the cartilage cells in it.
The new cartilage cells obtained after this procedure, which lasts for a few weeks, are transplanted to the damaged area by open surgery. In cartilage transplantation techniques, these cells are injected under a membrane-shaped tissue which taken from around the knee and sutured to the damaged area.